What is a Sitemap?
A sitemap is a page within a website that works as an index, categorising the other pages contained therein. Sitemaps have a positive impact on a website’s SEO by giving information to web crawlers. Web crawlers are bots managed by search engines (Google, Bing, etc.) which locate your website’s content. Sitemaps actually work together with web crawlers and help them understand your site’s structure and easily find its content.
Sitemaps are extremely useful in search engine optimisation. How? By allowing search engines to read and intelligently crawl the pages on your site. Sitemaps give web crawlers a variety of information in order to accomplish this. For example, how important each page of your site is and which is its priority ranking? When was it last updated and how often is each page updated?
There are two main types of sitemaps: HTML and XML. HTML sitemaps mainly guide the visitors through a website. XML sitemaps guide search engine bots to ensure they find a website’s URLs in the index.
HTML sitemaps
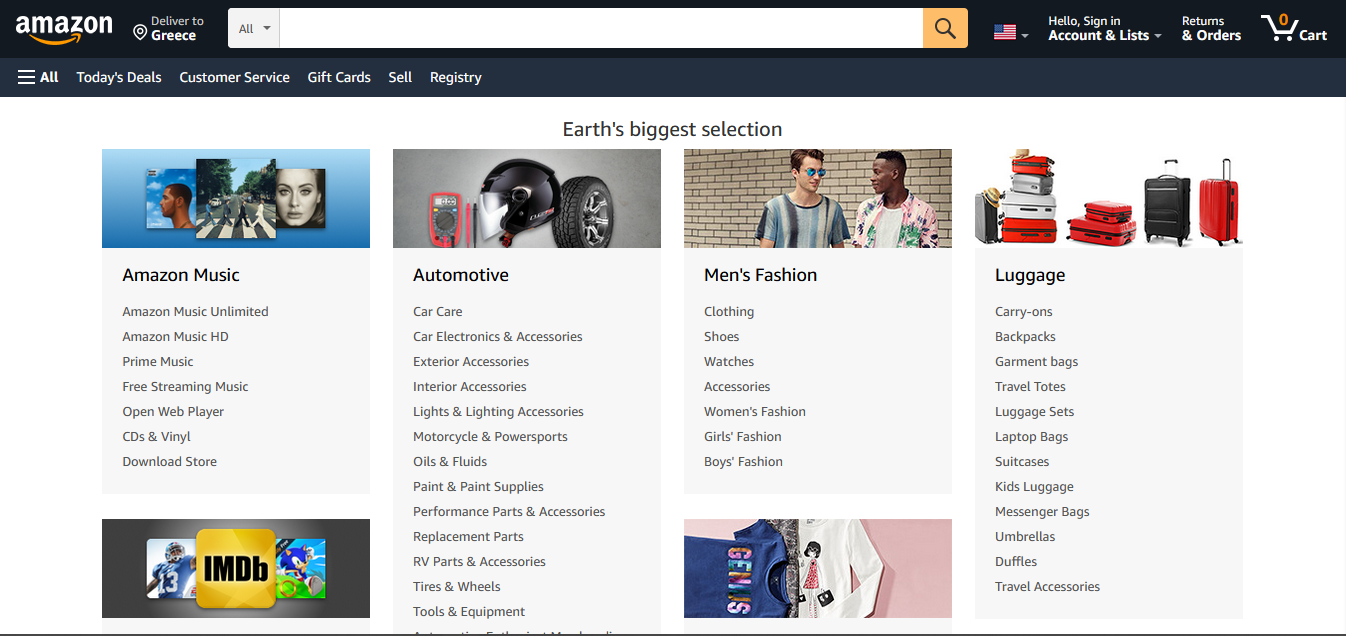
An HTML sitemap is a link usually located at the bottom of a website. All the other pages are included in the sitemap to show visitors what is included in your website, in an easy and visualised way. HTML sitemaps are usually of limited value to SEO. They are mainly used to improve navigation and therefore, user experience. Some very large websites have a dedicated page for this, leading users to their most visited and useful pages. A great example of an organised sitemap can be found at amazon.com. This sitemap contains all the major categories, as well as the most important subcategories, making it easy for users to search for products they are looking for.
XML sitemaps
XML sitemaps are XML (Extensive Markup Language) files specifically designed for search engine bots. The XML code in the file guides the bot within the website and helps it understand the relationship between each page.
Why are XML sitemaps important?
Search engines can crawl your website even if you do not have an XML sitemap. However, creating a sitemap has significant advantages in SEO which makes it a powerful tool for your online presence.
How can XML sitemaps benefit your SEO?
- This type of sitemap guides the search engine to crawl every page on your site and index it. There is a chance that search engines won’t find any content at all. This can happen especially on websites with complex “architecture”, where the content is hidden in deeper pages. A sitemap ensures that crawlers will include these pages as well.
- XML sitemaps show the search engine which pages have priority on your website. You can do this by including a tag on the sitemap stating which pages are the most important. Therefore crawler bots will focus on these pages.
- It helps search engines to be more direct and effective during the indexing process. Search engines can now very quickly discover and index information and data for new pages. This allows them to give us relative and high quality results when we do a search. A sitemap contributes significantly to the search engines capturing the data of your pages.
- The XML sitemaps provide search engines with a lot of additional information about your website. You can include optional tags that give search engines more data to make crawling the site easier. For example, “changefreq” tells the bot how often your page is updated, while “lastmod” tells the search engine when you last changed it.
- Sitemaps also provides you with information about the Googlebot activity, through Google Webmaster. It is a free tool that helps you evaluate and maintain your website performance in search results.
- An XML sitemap can also remove duplicates from your website. You may have duplicate content on your site, without realising it. This is bad news for your SEO. Duplicate content is removed while using a sitemap.
- It helps large websites, with a lot of content, to organise their indexing in a way that will attract the search engines.
An XML sitemap is highly recommended for:
A new site: sitemaps will help crawlers find a new site and index its pages faster. This will help in starting to appear faster, in search results.
A big website: when we say big we mean a site with thousands to millions of pages. For websites of this size, Google is dedicating a specific Crawl Budget. That is, a certain number of pages that Googlebot crawls and indexes within a given time frame. The sitemap will help make this whole process more efficient for bots, ensuring that each new or updated page appears in the results faster.
Sites that frequently update their content: ff you are constantly changing the content of your website, a dynamic XML sitemap will help new crawlers index new content in search engines.
You want to make sure that once your site is up and running, Google – by far the most popular search engine – will have access to your XML sitemap as soon as possible. For more specific tips on what to include on your sitemap and how to submit it to Google, follow the tips at the following link.
How to create HTML sitemaps
First, think whether your site needs a sitemap. The main goal with an HTML sitemap is to improve the navigation for your users and, consequently, their experience. For small websites, navigation is usually easy and therefore you don’t need extra help. Start by gathering your most important pages’ URLs. Then, you just need to restructure the footer and add links to these pages. Make sure the sitemap section is easy to read so that your users can find what they are looking for.
How to create XML sitemaps
You don’t need technical skills to do it! There are many tools that can create a sitemap for you. For WordPress websites you can simply use the Yoast SEO Plugin. Not only will it create a sitemap for your website, but it will also update it automatically when you add or remove pages. If this doesn’t suit your needs, check out the sitemap tools list here. Of course, do not forget to submit it to Google Search Console as soon as you create it!
Good luck!







Join the Discussion